Boosting your website's SEO and organic search performance
Learn how to improve your website's SEO quickly and easily with three simple actions. Boost organic search performance and gain more visibility with these tips.
In the tech industry, SEO is a term that probably everyone heard of at least once, but what is SEO? Search Engine Optimization (SEO for short) is optimizing a site's configuration, content, and link relevance to perform better when using search engines. In many cases, improvements in search engine optimization offer a better user experience and search results. The common goal of any website or business owner is to gain more visibility and a wider reach. By performing optimizations, keyword research and analysis, and content planning, administrators can boost a site's performance in the eyes of search engines.
A simple website owner, such as a developer with a portfolio or a startup, won't have the resources to create an entire SEO strategy or pay for the latest research and analysis tools. This guide is aimed at those owners and describes how you can take three simple actions to boost your website's SEO quickly and easily. Search engine optimization should be a focus point, even at different scales. I will describe how by implementing the correct schema markups, SEO checks, and blog posting strategy, you will be able to boost SEO and organic search performance.
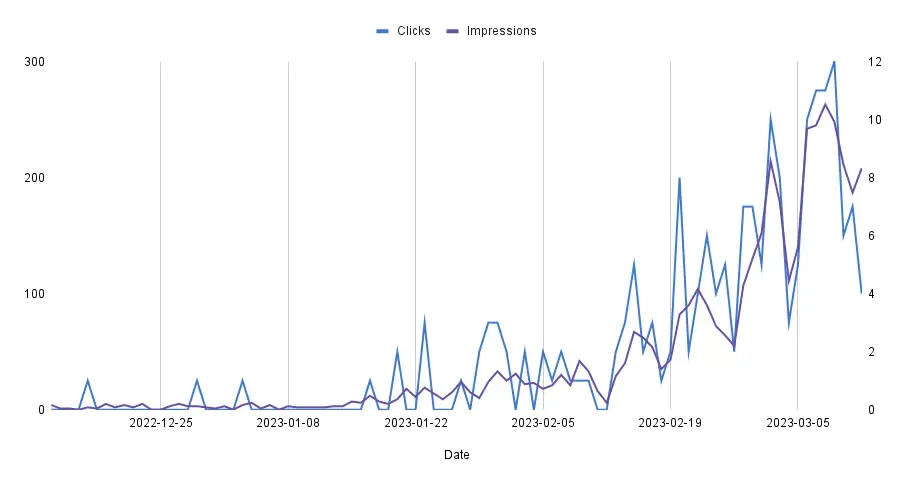
As you can see in the image above, my portfolio has significantly improved in organic search traffic, search result performance, and search engine ranking after implementing these actions.
Implementing a schema markup
What is a schema markup?
Schema markup, also known as structured data and found in Schema.org, is the way you can help search engines understand your site and its content. There are many encodings, including RDFa, Microdata, and JSON-LD, in which you can write your structured data. It covers most entities or relationships you will probably need, although you can extend it if necessary.
How does a schema markup work?
A schema markup should be available for the search engine crawlers, the robots that scan the whole internet. These robots look for them when they crawl your site. Schema markups should be available at that time. It is one limitation you should factor in when choosing your front-end stack. My guide on Static Site Generation can help you understand why that matters. You define the content of your structured data, and the bots will account for it when indexing your site.
How does a schema markup improve your SEO?
On one end, when using the Google Search Console, sites implementing specific markups get performance boosts. As you provide the search engines with more information about your website, search engines trust you more and are confident when showing your results. Also, by implementing relevant keywords in your schema markups, search engines can yield better results.
On another end, schema markups enable special SERPs (Search Engine Results Pages), which are the responses to a user's search query. These snippets, like the FAQ, recipe, or movie snippets, can increase visibility and user experience.
What types of schema markups are there?
Google uses only a subset of the many structured data types on the Schema.org page. I'll list a few of them (the ones I use), but I recommend reading the entire list on Google's documentation:
- Article: Used for articles, news, and blog post. Enables Google to offer better title text, images, and date information results on Google Search.
- Breadcrumb: Used to indicate the position in a site's hierarchy and helps users navigate a website effectively.
- FAQ: Used when the page contains questions and answers for a particular topic.
- Logo: Specify the organization's logo and general information for the Google Search knowledge panel.
These are the most commonly used ones, but if your website justifies using any of the others, you should go ahead and implement them.
How can you implement schema markups?
You can quickly implement schema markup in self-hosted and most hosting-based deployments by following the format and adding the correct script tag in the HTML head. It is known as the JSON-LD format.
<html>
<head>
<title>Example Site - Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "FAQPage",
"mainEntity": [
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What should FAQ include?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "An FAQ page (short for Frequently Asked Question page) is a part of your website that provides answers to common questions, assuages concerns, and overcomes objections. It's a space where customers can delve into the finer details of your product or service, away from your sales-focused landing pages and homepage."
}
},
{
"@type": "Question",
"name": "What is the difference between FAQ and Q&A?",
"acceptedAnswer": {
"@type": "Answer",
"text": "In FAQ Schema one question has only one answer but in Q&A schema, one question may have multiple answers. For example, let's take the example of What are the top 11 SEO Tools Every Marketer Should Use in 2020."
}
}
]
}
</script>
</head>
<body></body>
</html>
In other options, like Microdata, you embed the properties directly in the HTML code for the specific schema. The JSON-LD format is usually more human-readable, making it more friendly.
You can test your schema markup configuration with the Rich Results Test from Google or the Schema Markup Validator from Schema.org. It is important to note that the markup should be available for search engine crawlers in the HTML file, these crawlers don't load JavaScript, so Single Page Applications should account for this.
Conducting SEO checks
It is essential to monitor your current site's SEO status continuously. It provides an opportunity to identify and correct any technical or content-related issues that prevent your site from achieving optimal search engine visibility and ranking.
What do I verify in an SEO check?
SEO audits involve checking for multiple factors like:
- Broken links lead search engines to believe your site has poor quality and might frustrate users.
- Page speed is a ranking factor. It can impact your search engine performance.
- On-page optimization factors like the meta title, meta description, and other header tags improve search appearance. Content keyword research is critical as well.
- Mobile-friendliness of pages is a factor taken into account by Google Search Console. Non-mobile-friendly pages won't get mobile results, which account for 60% of traffic.
- Accessibility and core web vitals help improve user experience on your web page. Tools like PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse can assist you when identifying issues with the Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS). Accessibility features like alt text for images are essential for the accessibility tests. You can read about my guide to Nuxt 3 caching to improve performance and boost your page speed result.
Note that it is not an exhaustive list of verifications, but a comprehensive SEO check can discover issues that affect your organic search results. Fixing these issues should be your top priority before optimizing the content itself. Tools like checkbot.io allow you to perform a comprehensive SEO check on existing websites for free! The next step in your SEO strategy after conducting a local SEO check to verify implementation errors is to perform keyword research and analysis.
What is keyword research and analysis?
It refers to analyzing the key phrases and terms your target audience searches. This process can look at the existing competition for terms and keyword gaps. The aim is to understand what your audience searches for and see their popularity and ranking difficulty in search engines.
By performing this analysis before (or after) creating your content, you can restructure pages to cater to the specific terms you want to compete. This process is part of search engine optimization and content marketing strategies.
There are several types of analysis available (not an exhaustive list):
- Keyword research and discovery are possible with tools like Google Ads' Google Keyword Planner and MarketMuse, where you can explore and test keywords. Although those tools can be expensive, they provide free tiers that are more than capable of getting the job done, with limitations. These tools perform a competitive analysis too.
- Search term analysis is available in Google Analytics and the Google Search Console. You can analyze the terms with which people are searching and landing on your page. By understanding how users find your page, you can optimize it further on those terms and gain authority. Google Trends is another tool that can help you understand the popularity of a search term.
- A competitive keyword analysis is available using the above tools for keyword research. A more rudimentary approach is possible too. You can search for the term in Google and copy the complete content of the first 10 to 20 results. Using a word cloud generator with that content can yield a keyword phrase analysis on your competitors, but it is more time-consuming.
After performing a keyword analysis and discovery, gathering all the information you need to create content that will attract organic search traffic, content optimization is the next step.
What is content optimization?
This process involves optimizing your web page for users and search engines. There are several factors to account for here: writing compelling headlines and descriptions, using keyword phrases throughout the content (without actually stuffing it with keywords), and image and multimedia resources optimization. You should have high-quality content that's engaging for users.
The next and last step of your SEO check process is link building.
What is link building, and why is it important?
Link building is an essential part of search engine optimization, as it helps establish your website's authority and credibility in the eyes of search engines. It requires other sites to link to your web page. It is a complicated and time-consuming process that possibly requires an SEO expert. Apart from a great deal of analysis and optimization needed, one can help link building by implementing guest writers and shareable content on social media.
Adding a blog post
It might seem trivial initially, but most results we obtain using search engines come from blog posts, articles, or news. What better way to increase your search visibility on specific topics than creating a blog post where you can discuss your company's or personal insights? By adding a blog, you will boost your organic search engine results and gain authority and help link-building at the same time. That is why many startups and digital marketing agencies work on blogs as part of their SEO strategy and use this fantastic SEO tool.
How can you create high-quality blog content?
Start by choosing a topic you have experience with and feel comfortable writing about in an article. You should then perform a keyword analysis and research to refine the specific topic you are targeting and the most used words by the competition. MarketMuse can help you with content planning to create a content SEO strategy. Grammarly can take your writing to the next level by ensuring it is not full of grammatical errors. You can take advantage of the free tier for both tools.
With all this research, you should be able to write compelling content for your users while optimizing your writing.
How to optimize a blog post?
The optimization of a blog post is a process that makes use of everything I mentioned above. The following are the main actions you can take to take your blogs to the next level:
- Implement schema markups. The
Articleschema should be present to signal search engines that your content is a blog post. Blog pages are a fantastic opportunity to includeBreadcrumbschemas on your page. Blog posts have the potential forFAQandHow-Toschemas.FAQschemas are generally more appropriate, although it depends on the content. - Perform keyword research and analysis on competitive terms. Analyzing keywords and competitive phrases can help you create high-quality content.
- Link building with both external and internal links. Leverage the relationships between your existing content by linking to your internal pages to drive engagement. Adding a "Read Next" section where you link to other posts can drive engagement up too.
- Implement a Table of Contents (ToC) to improve your SERP. According to Search Engine Land, including a ToC can help Google create specialized SERPs for your search results. It is a simple yet effective way to improve user experience as well.
- Index your pages on Google Search Console to yield better search engine results.
- Implement the correct tags for OpenGraph and Twitter cards. Tools like opengraph.xyz allow you to visualize all your web page share cards. It is a fantastic tool for debugging social media share cards.
Sharing your blog posts on social media can boost your organic search too. A compelling title tag and meta description are essential for your share cards to drive click-through performance results.
What specific results have these strategies yielded?
I have been working on my portfolio for years, implementing Google Analytics and Search Console as part of my SEO strategy. After paying more attention to what I mentioned above, my organic search performance has skyrocketed.
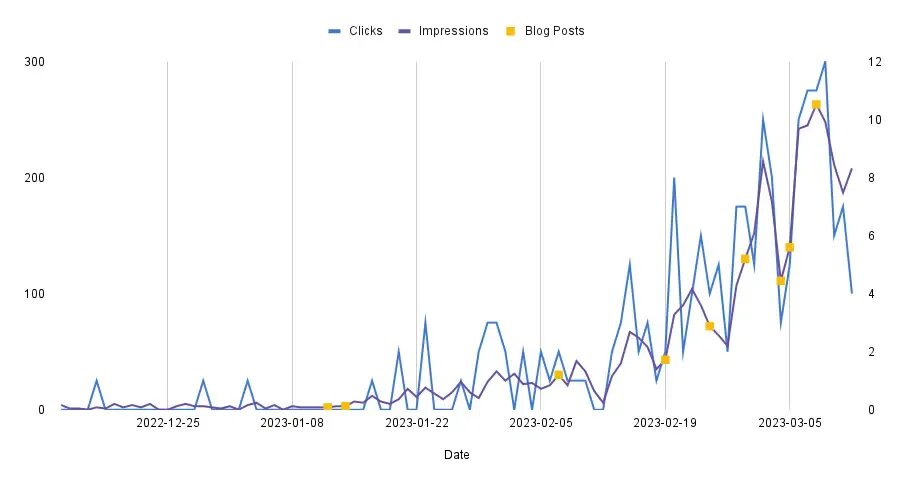
As you can see in the image below, after implementing blog posts and publishing each post, engagement, and impressions from organic search results increase.
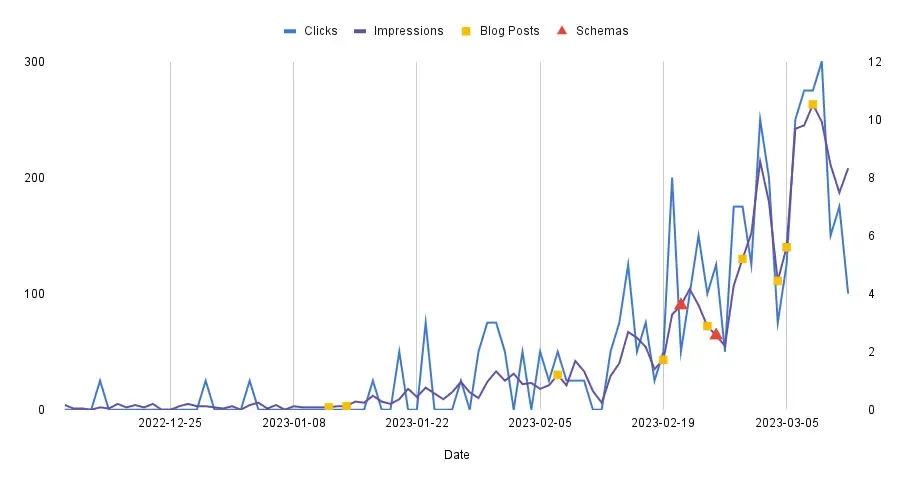
Correcting schemas and implementing the Logos and FAQ schemas have improved my search engine results.
Consistently uploading blog posts drives more engagement for my content and portfolio, improving my presence and authority in the topics I discuss.
Closing thoughts
By implementing the strategies I describe in this guide: including schema markups, conducting regular SEO checks, and adding a blog post to your site, you can boost your SEO and organic search performance across multiple search engines. These are the SEO basics you need to grow your business and gain good SEO. More complex technical SEO concepts are out there, but the basics will serve you well as a starting point.
I recommend you implement at least one of these recommendations (the more, the merrier), as it will help you regardless of whether you are a digital marketing agency or an individual. I have guides on other topics you might be interested in, so check out the blog!
